Es importante resaltar que el manejo derivativo quirúrgico es una opción valida, vigente y que cobra fuerza. Ante la evidencia disponible, el tipo de derivación debería escogerse a la luz del pronóstico, variaciones anatómicas y experiencias quirúrgicas 41; pueden salvar la vida del paciente y no contraindica posteriormente un trasplante hepático 42.
[enc_su_row][enc_su_column size=”1/3″]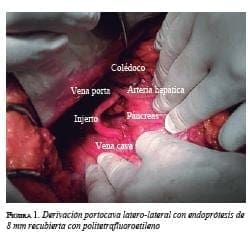 [/enc_su_column]
[/enc_su_column]
[enc_su_column size=”1/3″]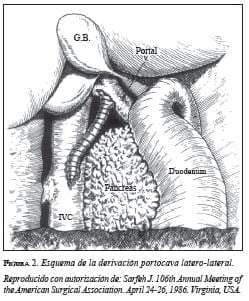 [/enc_su_column]
[/enc_su_column]
[enc_su_column size=”1/3″]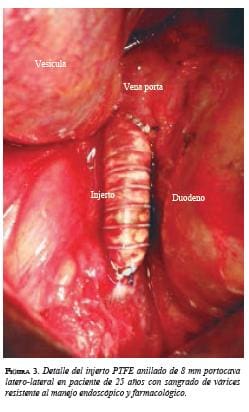 [/enc_su_column][/enc_su_row]
[/enc_su_column][/enc_su_row]
La decisión de llevar a cirugía depende de la respuesta al manejo médico y endoscópico instaurado 29, pero en caso de fallar, contemporizar su manejo de forma “expectante” usualmente conllevan a un deterioro clínico, hemodinámico, empeoramiento de su clasificación de Child, que influye directamente en morbilidad y mortalidad, por lo cual diferir este procedimiento disminuye la posibilidad de un desenlace favorable.
Portocaval Shunts in the Era of TIPS, Endoscopy and Liver Transplantation. Indications in Acute Esophageal Hemorrhage
Abstract
Portocaval shunts constitute a milestone in the history of the surgical treatment of portal hypertension. Bleeding from esophageal varices is a surgical emergency that demands immediate intervention. The endoscopic management of esophageal varices and the advent of TIPS, plus the development of liver transplantation have diminished the frequency of the use of portocaval shunts. However, these procedures have precise indications, both as emergency operations in some cases of esophageal varicose hemorrhage as well as elective procedures in selected patients with portal hypertension.
We hereby present a literature review of the “state of the art” of portocaval shunts motivated by a patient that was successfully treated at Hospital Occidente de Kennedy in Bogotá, Colombia.
Key words: portal hypertension; esophageal and gastric varices; gastyroiestinal hemorrhage; surgical portocaval Shunt
Bibliografía
1. Lillegard JB, Hanna AM, McKenzie TJ, Moir CR, Ishitani MB, Nagorney DM. A single-institution review of portosystemic shunts in children: An ongoing discussion. HPB Surg. 2010; 2010: 964597.
2. Kato T, Romero R, Koutouby R, Mittal NK, Thompson JF, Schleien CL, et al. Portosystemic shunting in children during the era of endoscopic surgery. J Pediatric Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000;30:419-25.
3. Wolff M, Hirner A. Current state of portosystemic shunt surgery. Langenbeck’s Arch Surg. 2003;388:141–9.
4. D’Amico G, Luca A. Natural history. Clinical-haemodynamic correlations. Prediction of the risk of bleeding. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1997;11:243-56.
6. de Franchis R, Primignani M. Natural history of portal hypertensionin patients with cirrhosis. Clin Liver Dis. 2001;5:645-63.
6. Rosch J, Keller FS. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: Present status, comparison with endoscopic therapy and shunt surgery, and future prospectives. World J Surg. 2001;25:337-46.
7. Banares R, Casado M, Rodríguez-Laiz JM, Camunez F, Matilla A, Echenagusia A, et al. Urgent transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for control of acute variceal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:75-9.
8. Rikkers LF, Jin G. Surgical management of acute variceal hemorrhage. World J Surg. 1994;18:193-9.
9. Orloff MJ, Orloff MS, Rambotti M, Girard B. Is portal-systemic shunt worthwhile in Child’s class C cirrhosis? Long-term results of emergency shunt in 94 patients with bleeding varices. Ann Surg. 1992;216:256-68.
10. Orloff MJ, Bell RH Jr, Orloff MS, Hardison WG, Greenburg AG. Prospective randomized trial of emergency portacaval shunt and emergency medical therapy in unselected cirrhotic patients with bleeding varices. Hepatology. 1994;20:863-72.
11. Warren WD. Presidential address: Reflections on the early development of portacaval shunts. Ann Surg. 1980;191:519-27.
12. Grinnell RS. Omentopexy in portal cirrhosis of the liver with ascites:A review of twenty-three cases. Ann Surg. 1935;101:891-901.
13. Ellis DS, Jones CM, Linton RR. The effect of venous shunt surgery on liver function in patients with portal hypertension; a follow-up study of 125 patients operated upon in the last tenyears. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1955;67:198-212.
14. Rypins EB, Milne N, Sarfeh IJ. Analysis of nutrient hepatic blood flow after 8-mm versus 16-mm portacaval H-grafts in a prospective randomized trial. Am J Surg. 1995;169:197-201.
15. Millikan WJ, Jr., Warren WD, Henderson JM, Smith RB, 3rd, Salam AA, Galambos JT, et al. The Emory prospective randomized trial: selective versus nonselective shunt to control varicealbleeding. Ten year follow-up. Ann Surg. 1985;201:712-22.
16. Rypins EB, Mason GR, Conroy RM, Sarfeh IJ. Predictability and maintenance of portal flow patterns after small-diameter portacaval H-grafts in man. Ann Surg. 1984;200:706-10.
17. Rikkers LF, Jin G, Langnas AN, Shaw BW Jr. Shunt surgery during the era of liver transplantation. Ann Surg. 1997;226:51-7.
18. Jenkins RL, Gedaly R, Pomposelli JJ, Pomfret EA, Gordon F, Lewis WD. Distal splenorenal shunt: Role, indications, and utility in the era of liver transplantation. Arch Surg. 1999;134:416-20.
19. Orozco H, Mercado MA. The evolution of portal hypertension surgery: Lessons from 1,000 operations and 50 years’ experience. Arch Surg. 2000;135:1389-94.
20. Henderson JM, Nagle A, Curtas S, Geisinger M, Barnes D. Surgical shunts and TIPS for variceal decompression in the 1990s. Surgery. 2000;128:540-7.
21. Collins JC, Ong MJ, Rypins EB, Sarfeh IJ. Partial portacaval shunt for variceal hemorrhage: Longitudinal analysis of effectiveness. Arch Surg. 1998;133:590-4.
22. Rosemurgy AS, Serafini FM, Zweibel BR, Black TJ, Kudryk BT, Nord HJ, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt Vs. small-diameter prosthetic H-graft portacaval shunt: Extended follow-up of an expanded randomized prospective trial. J Gastrointest Surg. 2000;4:589-97.
23. Rosemurgy AS, Molloy DL, Thometz DP, Villadolid DV, Cowgill SM, Zervos EE. TIPS in Florida: Is its application a result ofevidence-based medicine? J Am Coll Surg. 2007;204:794-802.
24. Ripamonti R, Ferral H, Alonzo M, Patel NH. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt-related complications and practical solutions. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2006;23:165-76.
25. Rosemurgy AS, Zervos EE, Bloomston M, Durkin AJ, Clark WC, Goff S. Post-shunt resource consumption favors smalldiameter prosthetic H-graft portacaval shunt over TIPS for patients with poor hepatic reserve. Ann Surg. 2003;237:820-7.
26. Punamiya SJ, Amarapurkar DN. Role of TIPS in Improvingsurvival of patients with decompensated liver disease. Int JHepatol. 2011;2011:398291. Epub 2011 Jul 2.
27. Rossle M. When endoscopic therapy or pharmacotherapy fails to control variceal bleeding: what should be done? Immediate control of bleeding by TIPS? Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2003;388:155-62.
28. Lopera JE. Role of emergency transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2005;22:253-65.
29. Bosch J, Berzigotti A, García-Pagan JC, Abraldes JG. The management of portal hypertension: Rational basis, available treatments and future options. J Hepatol. 2008;48(Suppl.1):S68-92.
30. Cadavid AJ, Santacoloma M, González RA. Estudio comparativo entre dos métodos de tratamiento del sangrado digestivo alto detipo varicoso. Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. 2000;15:161-4.
31. Chau TN, Patch D, Chan YW, Nagral A, Dick R, Burroughs AK. “Salvage” transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: Gastric fundal compared with esophageal variceal bleeding. Gastroenterology. 1998;114:981-7.
32. Johnson M, Rajendran S, Balachandar TG, Kannan D, Jeswanth S, Ravichandran P, et al. Transabdominal modified devascularization procedure with or without esophageal stapler transaction –an operation adequate for effective control of a variceal bleed. Is esophageal stapler transection necessary? World J Surg. 2006;30:1507-19.
33. Dagenais M, Langer B, Taylor BR, Greig PD. Experience with radical esophagogastric devascularization procedures (Sugiura) forvariceal bleeding outside Japan. World J Surg. 1994;18:222-8.
34. Selzner M, Tuttle-Newhall JE, Dahm F, Suhocki P, Clavien PA. Current indication of a modified Sugiura procedure in the management of variceal bleeding. J Am Coll Surg. 2001;193:166-73.
35. Borgonovo G, Costantini M, Grange D, Vons C, Smadja C, Franco D. Comparison of a modified Sugiura procedure with portal systemic shunt for prevention of recurrent variceal bleeding in cirrhosis. Surgery. 1996;119:214-21.
36. Romero-Torres R. Hemostatic suture of the stomach for the treatment of massive hemorrhage due to esophageal varices. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981;153:710-2.
37. Romero-Torres R. A new surgical approach for the treatment of massive hemorrhage due to esophageal varices. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 1981;22:555-60.
38. Romero-Torres R. Long-term results of hemostatic gastric suture in the treatment of esophagogastric varices. World J Surg. 1989;13:313-6.
39. Clark W, Hernández J, McKeon B, Villadolid D, Al-Saadi S, Mullinax J, et al. Surgical shunting versus transjugular intrahepatic portasystemic shunting for bleeding varices resulting from portal hypertension and cirrhosis: A meta-analysis. Am Surg. 2010;76:857-64.
40. Costa G, Cruz RJ Jr, Abu-Elmagd KM. Surgical shunt versus TIPS for treatment of variceal hemorrhage in the current era of liver and multivisceral transplantation. Surg Clin North Am. 2010;90:891-905.
41. Aydin U, Yazici P, Kilic M. Porto-systemic shunt using adrenal vein as a conduit; an alternative procedure for spleno—renal shunt. BMC Surg. 2007;7:7.
42. Abou Jaoude MM, Almawi WY. Liver transplantation in patients with previous portasystemic shunt. Transplant Proc. 2001;33:2723-5.
Correspondencia: ERNESTO NIEVES, MD
Correo electrónico: ernestonieves1@me.com
Bogotá, Colombia
